Your basket is currently empty!
Closed loop sustainability
Designing a Sustainable Integrated RAS with Aquaponics, BSF Waste Management, and Efficient Shipping
In the evolving world of aquaculture, sustainability and efficiency are critical drivers for success. Integrating Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS) with aquaponics, Black Soldier Fly (BSF) waste management, and a focus on efficient fish processing and shipping creates a closed-loop, highly scalable system. Here’s how this innovative setup works, including visual cues for key processes and outputs.
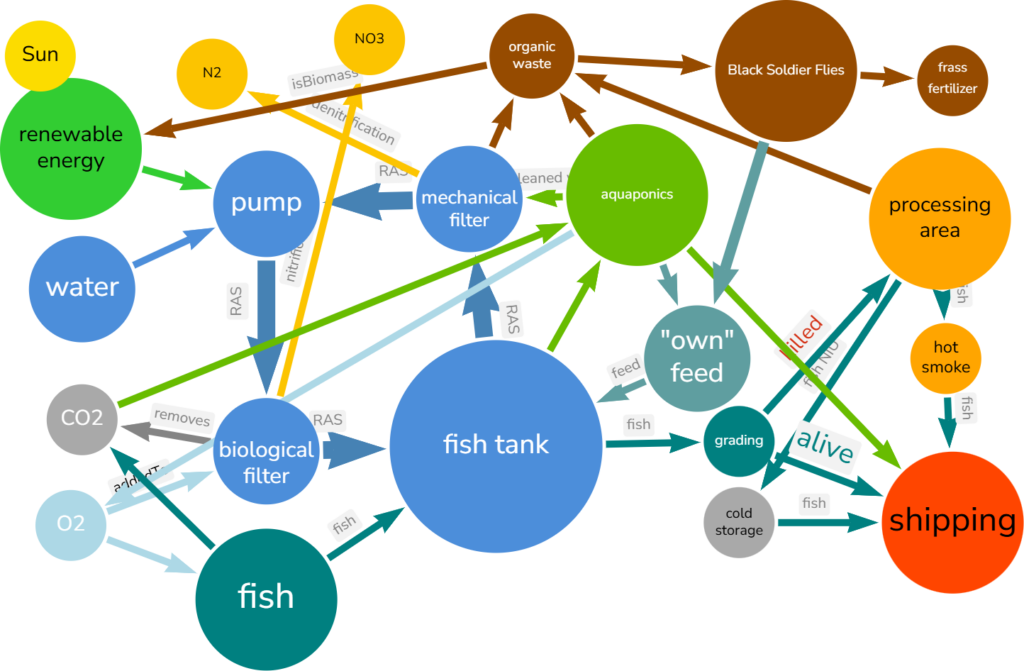
1. The Core System: RAS
At the heart of this setup lies the Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS), designed for maximum water efficiency and optimal fish health. Water continuously circulates between the fish tanks and filtration systems, reducing waste and conserving resources.
- Fish Tanks & Filtration: Fish, such as catfish or tilapia, are grown in controlled environments. Dissolved waste (e.g., ammonia) and solid waste (e.g., feces) are directed to filters for processing.
- Biological Filtration: Beneficial bacteria convert toxic ammonia into less harmful nitrates that can be reused in aquaponics.
- Gas Exchange: Oxygen is essential for fish and bacteria, while excess CO₂ is removed to maintain balance.
2. Vertical Farming: Aquaponics
The aquaponics system integrates seamlessly with RAS, utilizing nitrate-rich water to grow plants while cleaning the water for reuse.
- Aquaponics System: Vertical farming setups maximize space, growing crops such as tomatoes, cucumbers, or leafy greens.
- Nutrient Recycling: Plants absorb nitrates from the water, reducing nutrient buildup and improving sustainability.
3. Waste Management: Black Soldier Fly (BSF)
Solid waste removed from the fish tanks is processed in the BSF composting unit, turning waste into valuable byproducts.
- BSF Composting Unit: Black Soldier Fly larvae consume organic waste, reducing its volume by up to 80%.
- Outputs:
- Protein-Rich Larvae: Larvae can be reintroduced as a sustainable feed source for fish.
- Frass (Organic Fertilizer): A nutrient-dense byproduct used for plant growth in aquaponics or traditional farming.
Frass: A Key Byproduct for Soil Health
Frass is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and beneficial microbes, making it a powerful organic fertilizer. It improves soil fertility, structure, and microbial activity, helping regenerate degraded lands and boost crop yields. By incorporating frass into the system, farmers can create a sustainable alternative to chemical fertilizers, contributing to healthier soils and a reduced environmental footprint.
4. Processing and Humane Handling
Fish are harvested, graded, and processed for market demands. Incorporating humane handling methods enhances meat quality and aligns with ethical standards.
- Processing Area: Fish are sorted by size and quality, then processed (e.g., gutted, filleted). Byproducts can be converted into fish meal or compost.
- Cold Pool System: Fish are humanely euthanized in near-freezing water, reducing stress and preserving texture and taste.
5. Efficient Cold Storage and Shipping
Shipping is the main output of the integrated system, ensuring processed fish reach markets in pristine condition.
- Cold Storage & Shipping: Fish are vacuum-packed and stored in refrigerated facilities.
- Shipping: The final step, delivering high-quality fish to customers efficiently and sustainably.
Energy Management
Energy is a vital input across the entire system, powering pumps, aeration, and cooling systems.
- Energy Input: Non-renewable or grid energy used for essential operations.
- Renewable Energy: Solar panels or other renewable solutions reduce carbon footprints and operational costs.
Key Benefits of This System
- Environmental Sustainability: Reduces water and nutrient waste, uses renewable energy, and creates a circular economy.
- Scalability: Suitable for both small-scale and commercial operations with modular components.
- Profitability: Diversifies revenue through fish, plants, organic fertilizer, and value-added products.
- Ethical and Efficient: Humane fish handling and energy-efficient practices improve product quality and market value.
Summary
Designing a fully integrated system that combines RAS, aquaponics, BSF waste management, and an efficient processing and shipping framework is a blueprint for sustainable food production. This system aligns with global sustainability goals, reduces resource dependency, and provides economic opportunities for farmers by creating a circular economy.
Appendix: Color Codes for Components
This appendix provides clear references for color coding, enabling easy visualization and understanding of the integrated system. Let me know if you need further customizations or diagrams!
| Component/Process | Color Name | Hex Code | Short Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fish Tanks & Filtration | Blue | #4682B4 | Core aquaculture process with water recirculation. |
| Aquaponics System | Green | #32CD32 | Plant growth using nutrient-rich water from RAS. |
| BSF Composting Unit | Brown | #8B4513 | Organic waste processing for larvae and fertilizer. |
| Processing Area | Orange | #FFA500 | Fish grading, humane handling, and preparation. |
| Cold Storage & Shipping | Gray | #A9A9A9 | Refrigeration and delivery logistics. |
| Shipping (Main Output) | Red | #FF4500 | Final output of fish and plant products. |
| Oxygen (O₂) | Light Blue | #87CEFA | Essential for fish respiration and bacteria. |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Dark Gray | #696969 | Byproduct gas removed during aeration. |
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Yellow | #FFD700 | Neutral gas from denitrification processes. |
| Fish | Teal | #008080 | Represents the fish in the tanks. |
| Fish Feed | Blue-Green | #5F9EA0 | Sustainable feed for aquaculture. |
Leave a Reply